Privileged Task Automation
Take control of every privileged action
Privileged Task Automation empowers teams to securely automate high-impact tasks, reduce manual effort, and accelerate productivity -all with complete visibility and governance.
Challenge & solution
Is manual task execution slowing you down?
Organizations struggle to securely automate and delegate privileged tasks without exposing credentials, manual intervention, and inconsistent governance -slowing operations and increasing risk.
How Privileged Task Automation solves this
Centralizes workflow authoring, management and assignment in one repository.
Enables low-code drag-and-drop workflow configuration for privileged tasks.
Automates tasks without exposing privileged credentials to users.
Lets general IT staff execute tasks via secure workflows, no need for direct privilege.
Stores credentials & parameters securely and centrally for consistent updates.
Captures detailed audit logs and reporting for compliance and governance.
Validates task assignments and withdraws access dynamically as roles change.
Use cases
Automate privileged tasks & operationalize zero trust
SailPoint Privileged Task Automation helps organizations improve IT operations accuracy, efficiency, and governance by automating and delegating repeatable privileged tasks, while reducing security risks by keeping credentials hidden from users.
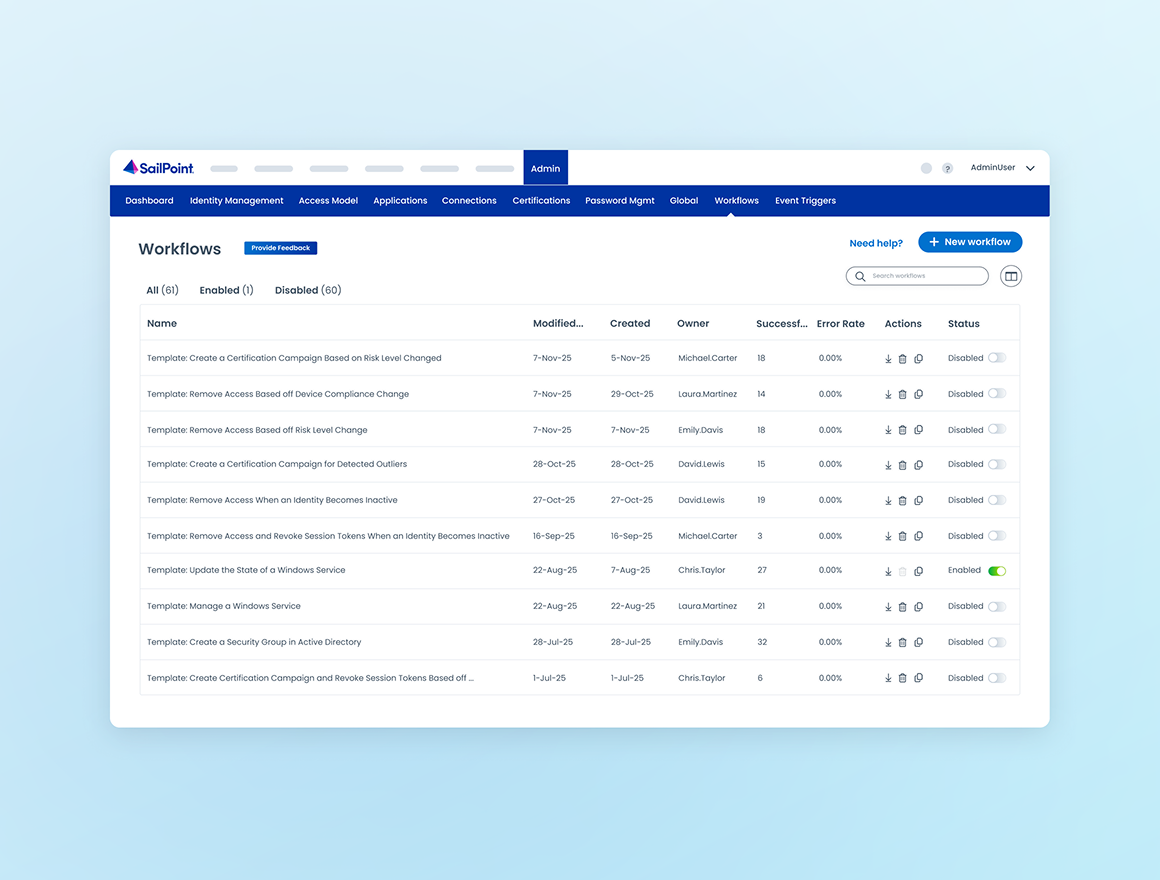
Boost productivity with easy, centralized workflow automation
Create automated workflows effortlessly in one central place, ensuring every process runs smoothly and consistently. Stay on top of execution with built-in visibility and auditing, while saving time with customizable, ready-to-use templates. Streamline your work, reduce errors, and boost efficiency all within Identity Security Cloud.
Securely delegate repeatable privileged tasks
Enable your teams to automate and delegate common, repeatable privileged tasks to general IT staff, without ever exposing privileged credentials. This delegation approach helps you reduce risky standing access, accelerate approval cycles and reduce manual errors. Built‑in governance empowers you to offer self‑service workflows from a centralized library, enforce role‑based execution, capture detailed audit trails and enforce policy. The result: operational efficiency and fast task completion with zero compromise to your security posture or regulatory compliance.
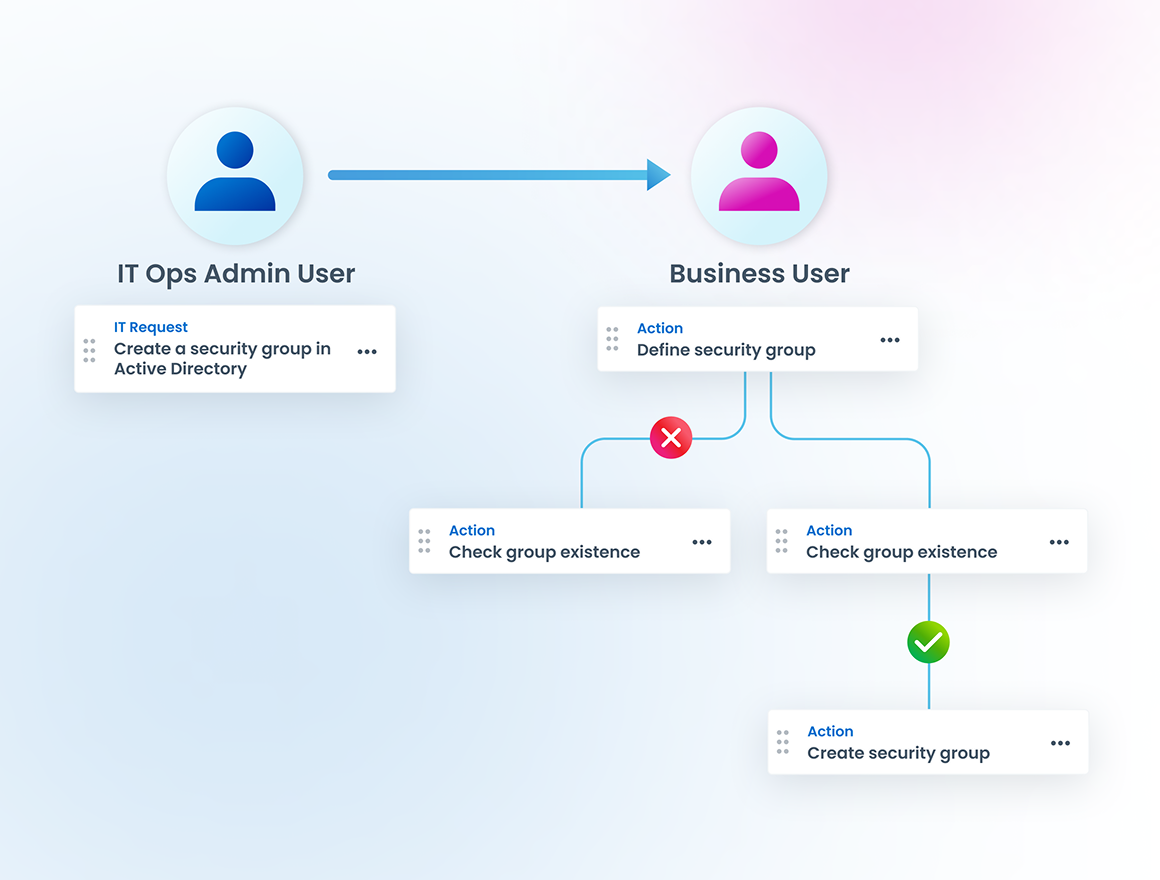
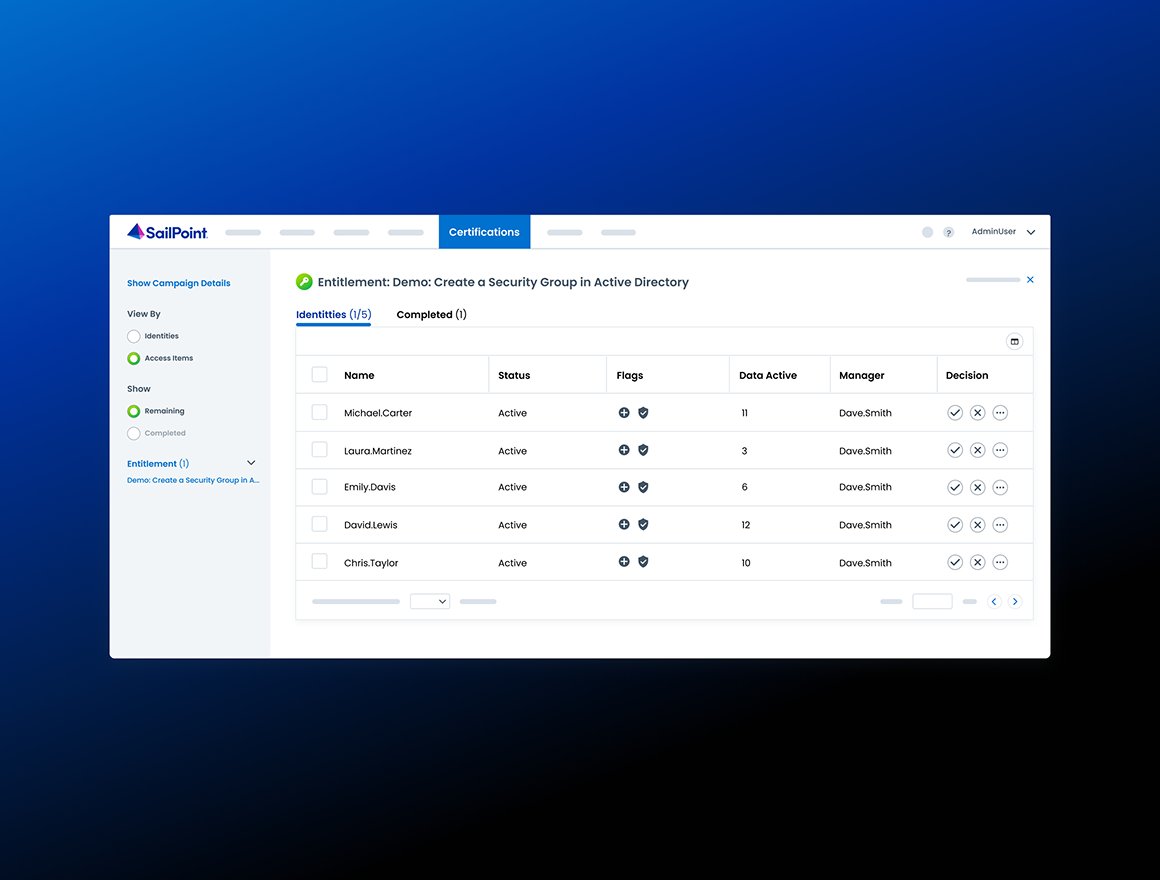
Ensuring oversight & compliance when automating privileged tasks
Automate complex, repeatable privileged tasks and enforce oversight, policy and controls without sacrificing speed. Privileged Task Automation built‑in governance means every task is created in a centralized library, assigned with precision, and executed without exposing privileged credentials. Your IT Ops staff can delegate workflows to broader teams, yet governance is maintained: task assignments are validated, access removed when roles change, and auditing data is captured for compliance. In essence, you gain efficiency and agility while reducing risk, eliminating standing privileges, and putting governance at the heart of privileged operations.
See SailPoint in action
Explore on your own
Take a self-guided tour of SailPoint's identity security platform
Take product tourRelated resources
Privileged Task Automation resources
Start your identity security journey today
SailPoint Identity Security Cloud empowers organizations to intelligently manage and secure real-time access to critical data and applications.
Advanced capabilities
Take your identity security solution even further
SailPoint Identity Security Cloud goes beyond the basics to tackle complex identity challenges. These specialized, add-on solutions offer even greater control and intelligence for reducing risk and ensuring compliance.
faq
Frequently asked questions
What are privileged tasks?
Privileged tasks in IT operations refer to activities that require the use of elevated permissions, typically granted through privileged credentials or privileged access. These tasks are usually performed by system administrators, network engineers, or other authorized personnel and involve high-level control over critical systems, networks, or applications.
What are some examples of privileged tasks?
Examples of privileged tasks include:
1. System Configuration and Maintenance: Installing, configuring, or updating system software, patches, or firmware on servers, databases, or networking equipment.
2. Access Management: Managing user accounts, roles, and permissions, including creating, modifying, or disabling accounts with elevated privileges.
3. Security Operations: Monitoring, configuring, and updating security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption mechanisms.
4. Data Management: Performing backups, restoring data, and accessing sensitive or confidential information.
5. Network Administration: Configuring routers, switches, VPNs, and other networking equipment that controls traffic and security within the organization.
6. Incident Response: Accessing logs, forensic data, and system configurations to respond to and mitigate security incidents or system failures.
7. Application Management: Deploying or modifying critical business applications, databases, and middleware that require administrator-level access.
8. Auditing and Monitoring: Accessing detailed system logs and audit trails to ensure compliance with security policies and regulations.
Because of the elevated risks associated with these tasks, strict access controls, logging, and monitoring are often implemented to ensure accountability and protect critical systems from unauthorized access or misuse.
Are there security risks associated with the execution of privileged tasks?
Executing privileged tasks in IT operations poses some security risks, primarily due to the sensitive nature of the activities and the elevated level of access required. Two key factors to watch for are:
- Risk of Credential Misuse or Theft Privileged credentials often have extensive access rights, making them prime targets for attackers. If these credentials are stolen, leaked, or misused, they can lead to data breaches, unauthorized system changes, or complete control over critical infrastructure. This can result in data loss, system downtime, compliance violations, and significant reputational damage.
- Risk Human Error and Misconfigurations Privileged tasks often involve complex configurations and system changes, which can introduce human errors or misconfigurations. These errors can unintentionally weaken security postures, cause downtime, or disrupt business services. Even minor mistakes can cascade into major incidents, making robust change management and audit processes essential.
Are there security risks associated with privileged credentials in automation scripts?
Embedding privileged credentials in automation scripts poses significant security risks to IT operations. These credentials, if stored without proper encryption or access controls, become easily accessible to unauthorized users, increasing the likelihood of theft or misuse. If a malicious actor gains access to such scripts, they can potentially execute privileged tasks, compromising critical systems, data, and infrastructure. Furthermore, clear text credentials embedded in scripts are vulnerable to exposure during code reviews, file sharing, or version control, where they can be inadvertently leaked. This lack of credential security not only violates best practices but also leaves organizations exposed to insider threats, external attacks, and compliance violations, amplifying the potential for data breaches, service disruptions, and reputational damage.
Is there a downside to not having a centralized repository for privileged tasks?
The absence of a centralized repository for privileged tasks and the reliance on individually authored scripts without execution oversight or audit introduce significant inefficiencies and risks within IT operations. Without a unified repository, tasks and scripts are often duplicated or inconsistently written, leading to redundant efforts and potential misconfigurations. This fragmentation can cause delays in identifying the most appropriate or secure scripts for particular tasks, hindering the ability to execute them efficiently. Additionally, the lack of oversight or auditing means that scripts may be executed without proper validation, exposing systems to errors, security vulnerabilities, or non-compliance with regulatory standards. Without a clear audit trail, it becomes challenging to track changes or identify the source of issues when things go wrong, complicating troubleshooting and undermining accountability. These inefficiencies not only slow down operations but also increase the risk of operational failures and security incidents.
Isn’t the execution of privileged tasks the sole responsibility of IT Operations?
Restricting privileged tasks execution solely to IT operations personnel can lead to backlogs and operational bottlenecks. This centralized control, while essential for security, can cause delays in routine processes such as system configuration, software updates, or access management. As general IT staff or business users must rely on specialized teams to perform these tasks, it creates a dependency that slows down operations, especially during peak periods or when critical issues arise. The limited availability of skilled personnel to handle all privileged tasks can lead to longer response times, reduced productivity, and frustration among users waiting for task completion. Furthermore, this bottleneck can prevent the organization from quickly adapting to changing needs or resolving issues in real time, potentially affecting business continuity. With the evolving IT landscape and fast-paced operations, it is difficult to keep privileged task execution within a single team, so it is recommended that organizations alleviate this burden by leveraging secure automation and empower other teams with self-service.
Contact us
Put identity security at the core of securing your business


